
摘 要:【目的】芦笋是百合科天门冬属植物石刁柏(Asparagus officinalis)的食用嫩茎,分析2个芦笋品种转录途径和代谢组成分,为深度评估芦笋营养价值和芦笋种质资源开发利用和品种选育提供理论依据。【方法】利用UPLC-MS对哥兰德和翡翠明珠2个芦笋品种的嫩茎并进行代谢组学研究,比较代谢组成分的种类和含量,分析芦笋转录途径和代谢组成分。【结果】共筛选出差异代谢物235种,占全部代谢物的13.03%,其中包括黄酮53种,氨基酸及其衍生物39种,酚酸类34种,木脂素21种,生物碱20种,脂质12种,有机酸8种,核苷酸及其衍生物7种,萜类7种,维生素6种,甾体5种,糖类4种,香豆素3种,酮类2种,醌类1种,醛类1种,以及其它12种。翡翠明珠与哥兰德相比,翡翠明珠的矢车菊素-3-O-半乳糖苷、没食子儿茶素-(4α→8)-没食子儿茶素、丁香苷、芥子碱、2-乙酰基-5-甲基呋喃与槲皮素-3-O-桑布双糖苷含量较高;哥兰德的葡萄糖基 5,8-二羟基-2,6-二甲基八碳-2,6-二烯酸,N-阿魏酰尸胺、毛蕊花糖苷、1-O-(6′-O-阿魏酰)葡萄糖苷-3-O-咖啡酰奎尼酸和知母皂苷 A3-葡萄糖苷含量较高。【结论】通过富集235种代谢物,得到次生代谢物的生物合成途径主要有氨基酸、辅助因子与黄酮类化合物的生物合成途径。
关键词:芦笋;LC-MS;代谢;转录途径
中图分类号:S63 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1001-4330(2024)10-2408-09
收稿日期(Received):2024-02-18
基金项目:天山英才-科技创新领军人才;新疆维吾尔自治区重大科技专项(2022A02005-2);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(KYYJ2022001);新疆蔬菜产业技术体系(XJARS-07)
作者简介:庄红梅(1987-),女,副研究员,研究方向为新疆特色蔬菜栽培与生理,(E-mail)zhuanghongmei86@163.com
通讯作者:王浩(1970-),男,山东济宁人,研究员,研究方向为蔬菜栽培与生理,(E-mail)wanghao183@163.com
王强(1983-),男,甘肃会宁人,研究员,研究方向为设施蔬菜栽培与生理,(E-mail)350615359@qq.com
0 引 言
【研究意义】芦笋是百合科天门冬属植物石刁柏(Asparagus officinalis)的食用嫩茎,营养均衡全面,维生素、蛋白质和人体必需氨基酸含量丰富,且富含多种黄酮类物质,具有抗氧化、抗菌、抗衰老和提高免疫力等生理活性以及药理作用,经常食用可消除疲劳、改善心血管功能、提高机体代谢能力,是一种食药兼用的蔬菜[1,2]。芦笋是多年生作物,栽培一次可连续采收十余年,因此品种的优劣对提高种植芦笋的效益有重要意义。【前人研究进展】超高效液相色谱串联质谱(Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry,UPLC-MS)技术是近年来常用于检测代谢物的方法,以其灵敏、高效、快速、检测范围广泛等特点而在植物活性成分的分析检测、产品品质差异分析等方面得到广泛应用[3]。【本研究切入点】不同芦笋品种均具有较高的营养价值,目前芦笋种质资源开发利用和品种选育文献尚较少。需利用UPLC-MS对哥兰德和翡翠明珠2个芦笋品种的食用嫩茎部分研究比较代谢组学。【拟解决的关键问题】研究芦笋转录途径和代谢组成分,深度评估芦笋营养价值,为芦笋种质资源开发利用和品种选育提供理论依据。
新疆农业科学第61卷 第10期庄红梅等:环塔里木盆地2个芦笋品种的代谢组学分析
1 材料与方法
翡翠明珠是山东华农芦笋科技有限公司新育成的杂交一代品种,综合性状优良,适合我国南北方种植,该品种丰产性强;哥兰德是美国加利福尼亚大学选育而成的杂交一代品种,属中熟品种,单产可达 1 500 kg/667m2,抗锈病能力强。翡翠明珠和哥兰德芦笋于 2019 年播种栽培于新疆和田洛浦县芦笋生产基地设施大棚中。成年后于采笋期(2022 年 10月)选取长度、粗度、笋形较为一致,无病虫害的芦笋带回实验室,通过超高效液相色谱串联质谱对芦笋中的代谢物进行定性定量检测,筛选出具有重要生物学意义和统计学显著差异的代谢物。
2 结果与分析
2.1 UPLC-MS/MS检测哥兰德和翡翠明珠芦笋代谢物成分对比
研究表明,用UPLC-MS/MS检测到哥兰德和翡翠明珠品种芦笋嫩茎中共有1 803种代谢物,包括黄酮260种(14.42%),酚酸类232种(12.87%),氨基酸及其衍生物214种(11.87%),生物碱188种(10.43%),脂质161种(8.93%),有机酸103种(5.71%),萜类97种(5.38%),甾体87种(4.83%),糖类79种(4.38%),核苷酸及其衍生物76种(4.22%),木脂素68种(3.77%),香豆素41种(2.27%),醌类28种(1.55%),维生素23种(1.28%),醛类14种(0.78%),酮类13种(0.72%),色酮类11种(0.61%),内酯类9种(0.50%),醇类9种(0.50%),茋类7种(0.39%),以及其它83种(4.60%)。图1
2.2 比较翡翠明珠与哥兰德芦笋代谢组成分的种类和含量
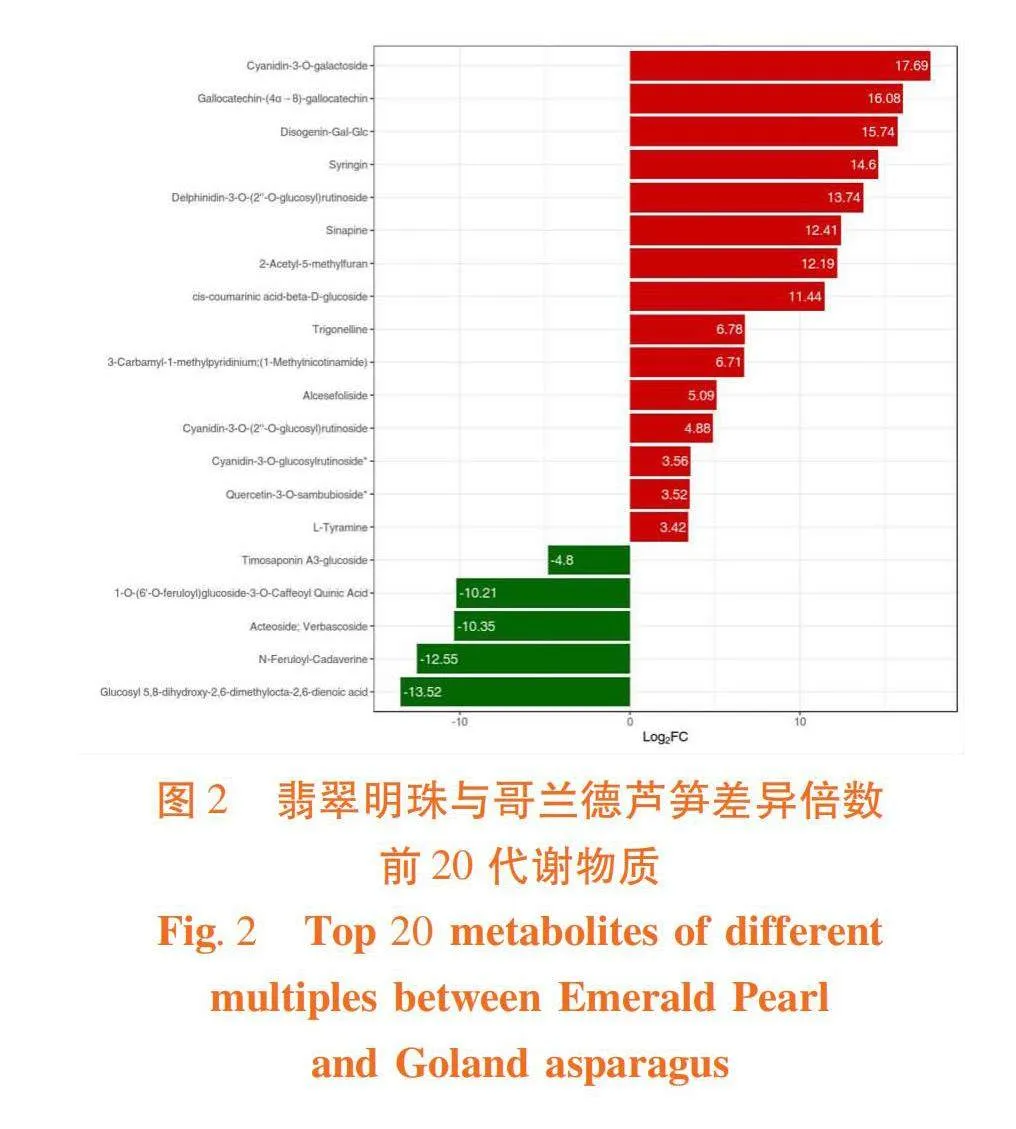
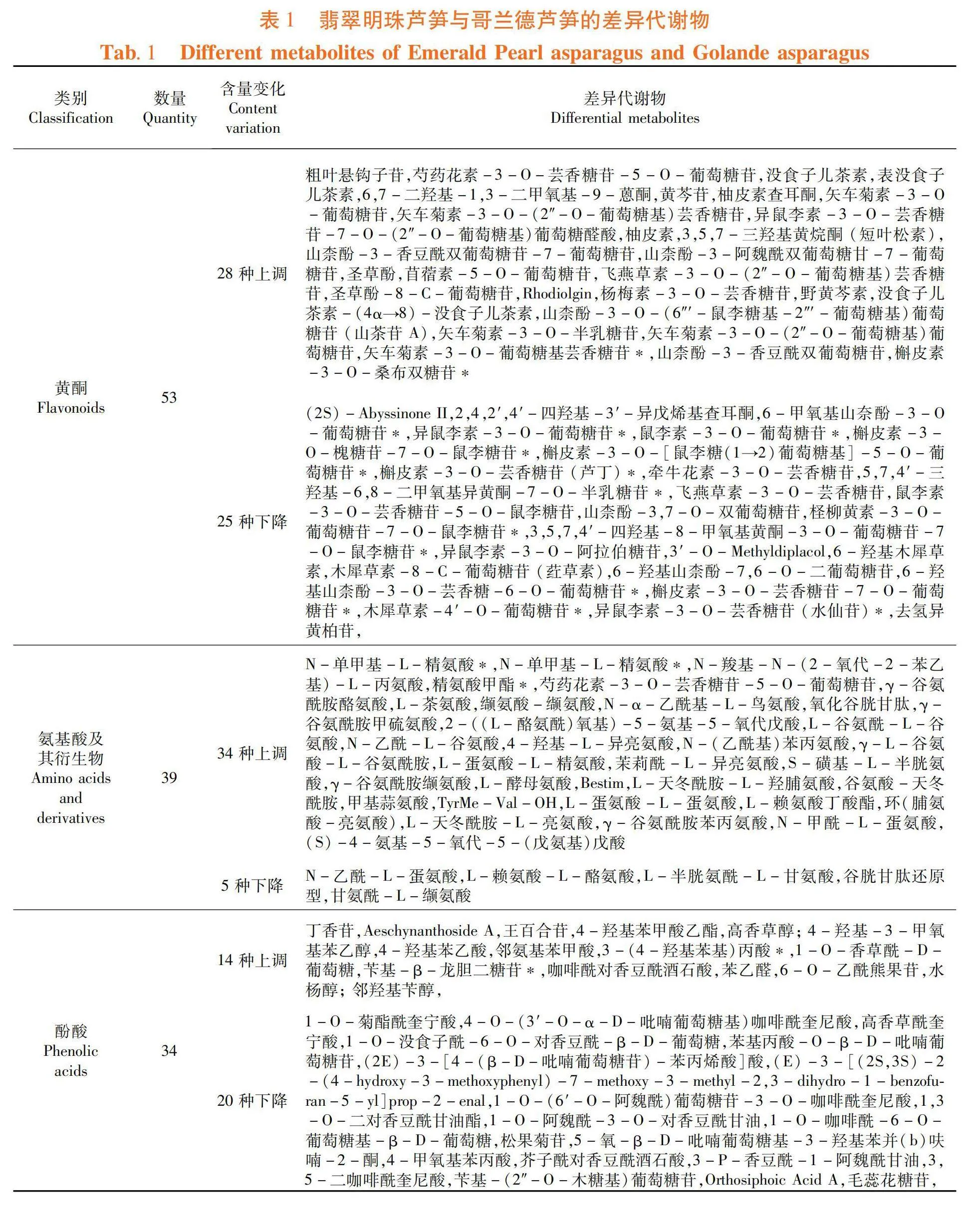
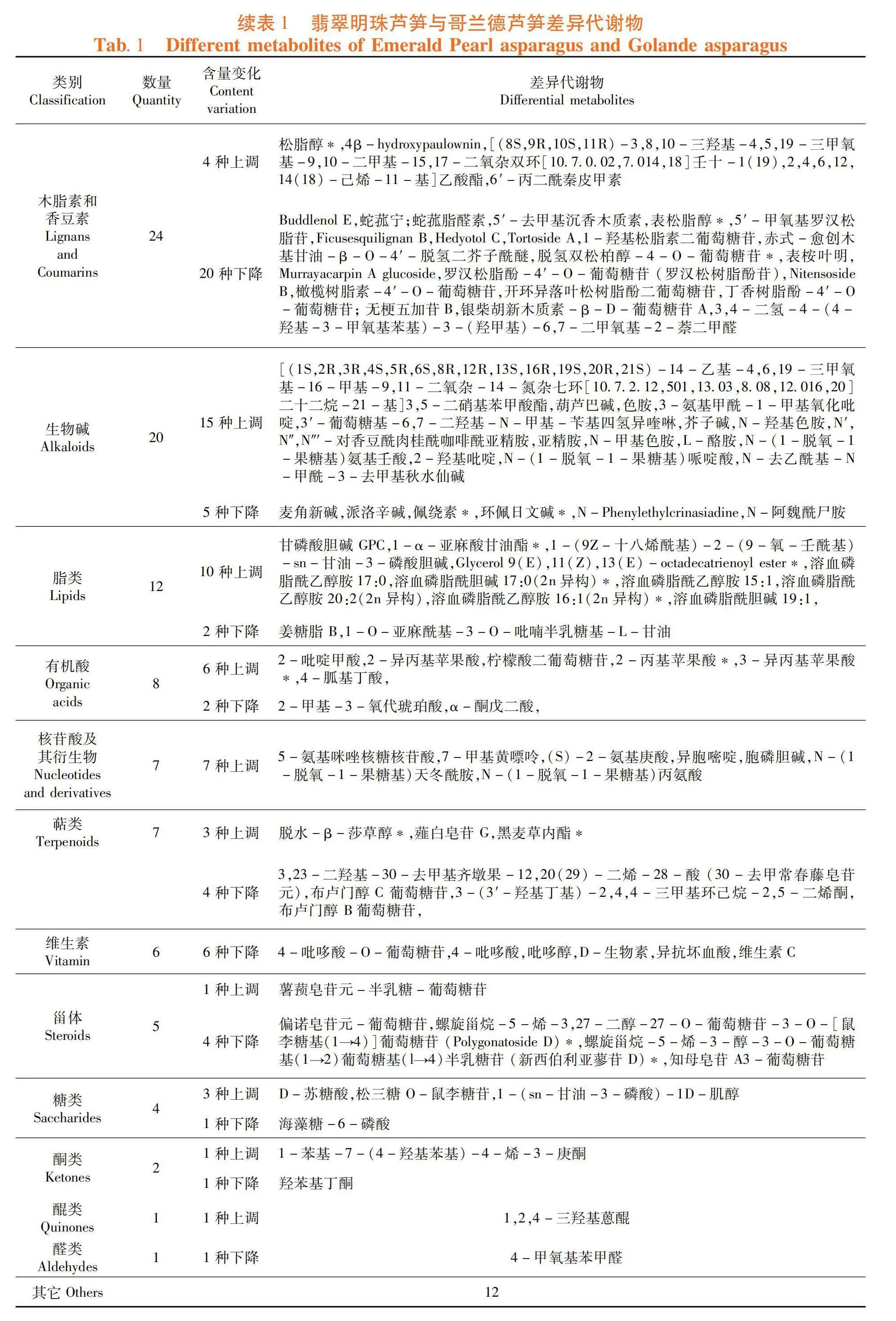
研究表明,共筛选出差异代谢物235种,占全部代谢物的13.03%,其中包括黄酮53种,氨基酸及其衍生物39种,酚酸类34种,木脂素21种,生物碱20种,脂质12种,有机酸8种,核苷酸及其衍生物7种,萜类7种,维生素6种,甾体5种,糖类4种,香豆素3种,酮类2种,醌类1种,醛类1种,以及其它12种。与哥兰德芦笋相比,翡翠明珠芦笋代谢组中有132种代谢物含量提高,103种代谢物含量下降,其中黄酮类物质中有28种含量上调,25种含量下降;氨基酸及其衍生物中有34种含量上调,5种含量下降;酚酸类物质中有14种含量上调,20种含量下降;木脂素和香豆素中有4种含量上调,20种含量下降;生物碱中有15种含量上调,5种含量下降;脂类物质中有10种含量上调,2种含量下降;有机酸中有6种含量上调,2种含量下降;7种核苷酸及其衍生物含量上调;萜类物质中有3种含量上调,4种含量下降;6种维生素含量下降;甾体物质中1种含量上调,4种含量下降;糖类物质中3中含量上调,1种含量下降;酮类物质中1种含量上调,1种含量下降,1种醌类物质和1种醛类物质含量下降。表1,图2
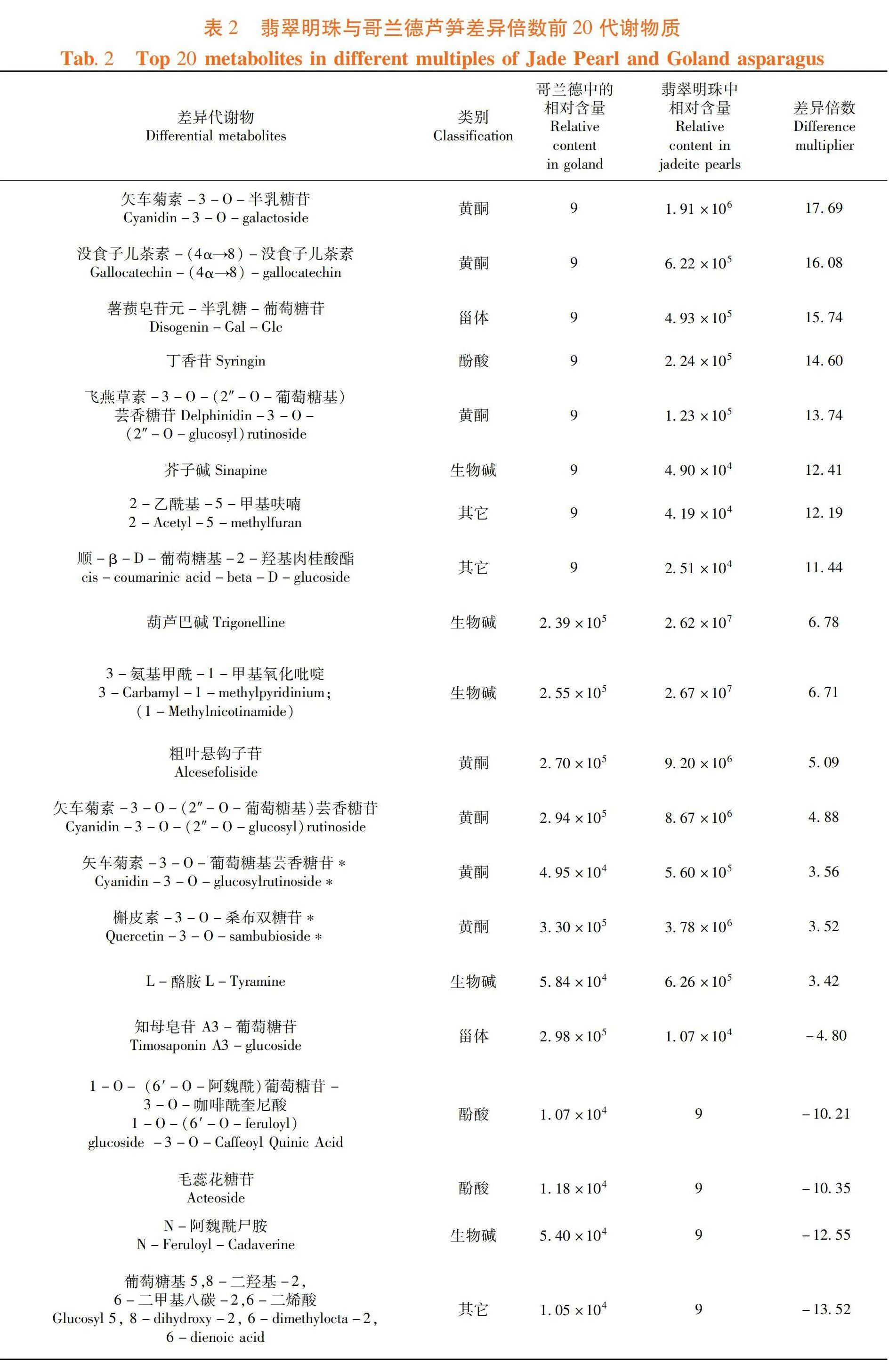
与哥兰德相比,上调差异倍数最高的代谢物是矢车菊素-3-O-半乳糖苷,其下依次为没食子儿茶素-(4α→8)-没食子儿茶素、薯蓣皂苷元-半乳糖-葡萄糖苷、丁香苷、飞燕草素-3-O-(2″-O-葡萄糖基)芸香糖苷、芥子碱、2-乙酰基-5-甲基呋喃、顺-β-D-葡萄糖基-2-羟基肉桂酸酯、葫芦巴碱、3-氨基甲酰-1-甲基氧化吡啶、粗叶悬钩子苷、矢车菊素-3-O-(2″-O-葡萄糖基)芸香糖苷、矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖基芸香糖苷、槲皮素-3-O-桑布双糖苷和L-酪胺;下调差异倍数最高的代谢物是葡萄糖基 5,8-二羟基-2,6-二甲基八碳-2,6-二烯酸,其下依次为N-阿魏酰尸胺、毛蕊花糖苷、1-O-(6′-O-阿魏酰)葡萄糖苷-3-O-咖啡酰奎尼酸和知母皂苷 A3-葡萄糖苷。表2,图2
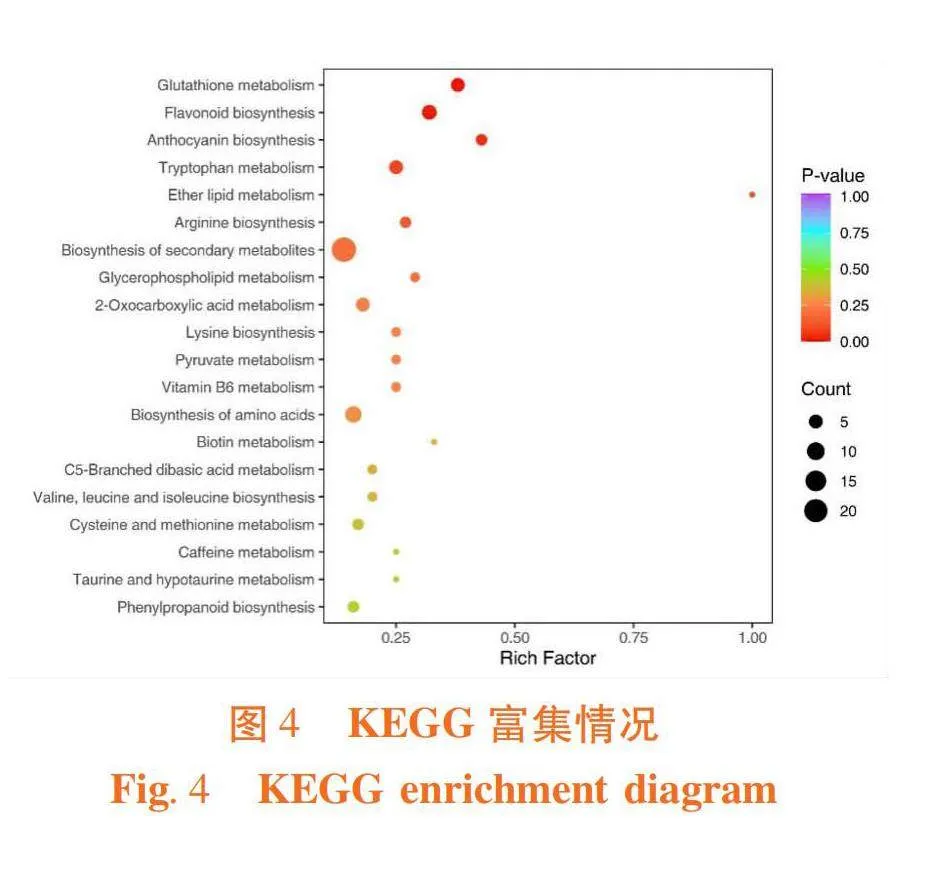
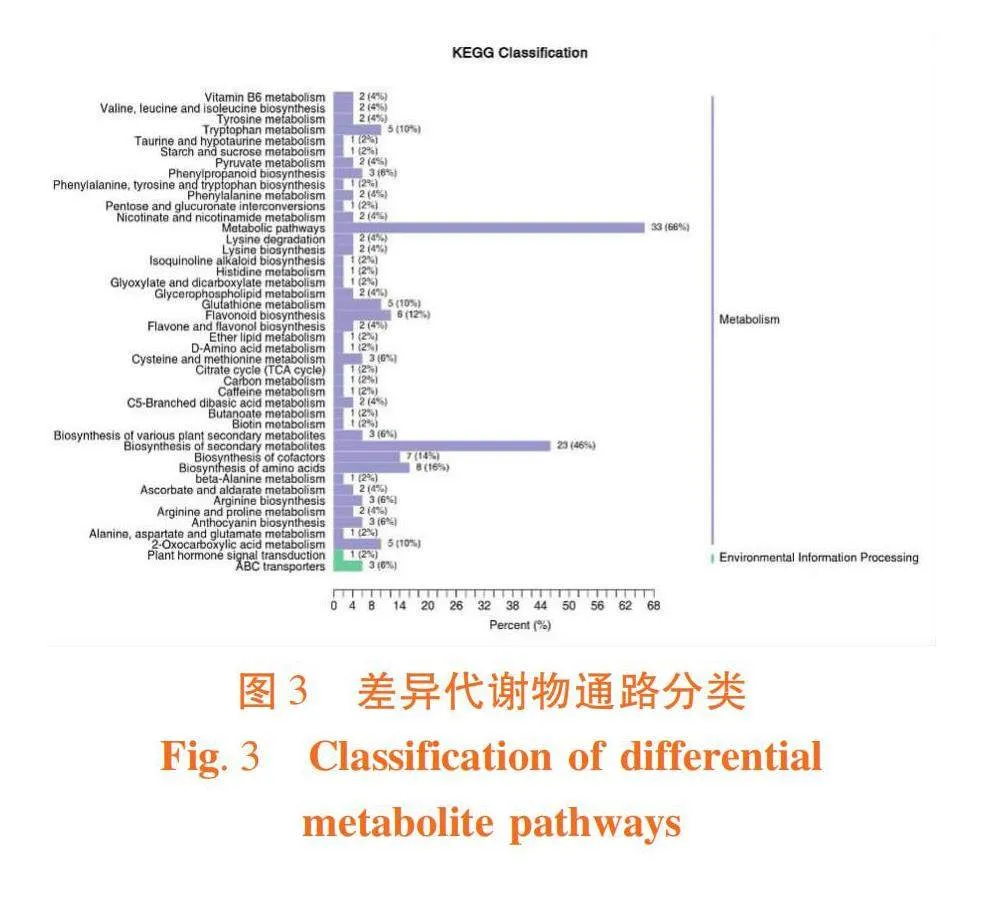
翡翠明珠、哥兰德的差异代谢物在44个KEGG通路中均有富集。代谢途径(Metabolic pathways)富集到的33个差异代谢物,数量最多,次生代谢物的生物合成途径(Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites)富集到23个差异代谢物,氨基酸的生物合成途径(Biosynthesis of amino acids)富集到8个差异代谢物,辅助因子的生物合成途径(Biosynthesis of cofactors)富集到7个差异代谢物,黄酮类化合物的生物合成途径(Flavonoid biosynthesis)富集到6个差异代谢物。图3
翡翠明珠芦笋中上调较高的差异代谢物丁香苷富集到苯丙烷类化合物的生物合成途径(Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis),芥子碱富集到苯丙烷类化合物和次生代谢物的合成途径,葫芦巴碱富集到烟酸和烟酰胺代谢途径(Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism),槲皮素-3-O-桑布双糖苷富集到黄酮和黄酮醇的生物合成途径(Flavone and flavonol biosynthesis,KEGG数据库网址:https://www.kegg.jp/)。图4
3 讨 论
3.1 在翡翠明珠芦笋中上调倍数最高的代谢物中,矢车菊素-3-O-半乳糖苷是一种广泛存在于多种蔬果中的花青素类物质[4];没食子儿茶素-(4α→8)-没食子儿茶素具有抗菌、抗氧化的功效[5];丁香苷具有抗炎免疫、保护肝功能的作用[6];芥子碱具有抗辐射、抗氧化、抗腹泻、抗癌、抗肿瘤、保护肝功能和降压平喘的药理作用[7];2-乙酰基-5-甲基呋喃是重要的食用香料[8];葫芦巴碱具有抗脱粒、抗糖尿病、抗氧化、抗炎和保护神经和心肾等功效[9,10];粗叶悬钩子苷具有抗氧化活性[11];槲皮素-3-O-桑布双糖苷能够促进对神经中枢的刺激,并具有抗氧化和抗癌活性[12]。在翡翠明珠芦笋中下调倍数最高的代谢物中,毛蕊花糖苷具有抗氧化、免疫调节、抗炎、保肝等生物活性和保护皮肤免受紫外线损伤的功效[13,14]。
3.2 此外,与哥兰德芦笋相比,翡翠明珠芦笋中还有许多其它具有药用价值的代谢物含量发生上调或下降。黄酮类物质中,黄芩苷、野黄芩素、柚皮素、圣草酚等含量上升,芦丁、荭草素、水仙苷等含量下降。黄芩苷能够具有显著的抗氧化、抗炎症、抗病毒活性,可显著抑制HIV逆转录酶的活性,并抑制HIV-1的复制[15];野黄芩素具有抑制结肠癌发生、抑制视网膜神经节RGC-5细胞凋亡等药理活性[16-18];柚皮素具有抗炎、抗凋亡、抗氧化应激等生物学活性,是潜在的治疗慢性肠道炎症性疾病有效药物[19,20];圣草酚具有抗氧化、降血脂、降血糖等功效,在抑制糖尿病肾纤维化、改善溃疡性结肠炎等亦有潜在的药用价值[21-24];芦丁具有抗炎、抗氧化、保护血管和镇痛等多种药理作用,且广泛应用在畜牧业中[25];荭草素具有抗癌细胞迁移,以及改善肺损伤、肝损伤以及细胞损伤等药理作用[26]。酚酸类物质中,松果菊苷等含量下降,松果菊苷具有抗炎、抗氧化、减轻脓毒症导致的心肌和肾功能损伤、治疗神经系统疾病的功效[27]。
4 结 论
通过富集235种代谢物,得到次生代谢物的生物合成途径主要有氨基酸、辅助因子与黄酮类化合物的生物合成途径。翡翠明珠与哥兰德芦笋上调和下调倍数最高的代谢物中的黄酮类物质具有显著的抗氧化、抗炎症、抗病毒活性,酚酸类物质具有抗氧化、治疗神经系统疾病的功效。
参考文献(References)
[1]杨晓春, 黎重阳, 张玲玲, 等. 响应面法优化绿芦笋罐头的生产工艺[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2023, 44(8): 82-88.
YANG Xiaochun, LI Chongyang, ZHANG Lingling, et al. Processing technology optimization of canned green Asparagus by response surface method[J]. Food Research and Development, 2023, 44(8): 82-88.
[2] 毛丽萍, 郭伟民. 芦笋营养价值与保健功能[J]. 食品工程, 2012,(3): 63-64.
MAO Liping, GUO Weimin. Nutrition value and health function of asparagus[J]. Food Engineering, 2012,(3): 63-64.
[3] Wu Y Q, Zhang C H, Huang Z J, et al. The color difference of rubus fruits is closely related to the composition of flavonoids including anthocyanins[J]. LWT, 2021, 149: 111825.
[4] Liang Z X, Liang H R, Guo Y Z, et al. Cyanidin 3- O-galactoside: a natural compound with multiple health benefits[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(5): 2261.
[5] Plumb G W, de Pascual-Teresa S, Santos-Buelga C, et al. Antioxidant properties of gallocatechin and prodelphinidins from pomegranate peel[J]. Redox Report: Communications in Free Radical Research, 2002, 7(1): 41-46.
[6] 胡闪闪, 胡红杰, 徐艳萍, 等. 紫丁香苷对LPS/D-GalN诱导的急性肝损伤的保护作用研究[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2023, 55(4): 120-126.
HU Shanshan, HU Hongjie, XU Yanping, et al. Protective effect of syringin on LPS/D-GalN induced acute liver injury[J]. Animal Husbandry amp; Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 55(4): 120-126.
[7] 杨占婷, 张得钧. 芥子碱的研究进展[J]. 华西药学杂志, 2017, 32(6): 658-661.
YANG Zhanting, ZHANG Dejun. Research progress of sinapine[J]. West China Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2017, 32(6): 658-661.
[8] 孙宝国, 李勇. 2-乙酰基-5-甲基呋喃的合成研究[J]. 精细化工, 1993, 10(6): 13-15.
SUN Baoguo, LI Yong. A new method for the synthesis of 2-acetyl-5-methylfuran[J]. Fine Chemicals, 1993, 10(6): 13-15.
[9] Ilavenil S, Kim D H, Jeong Y I, et al. Trigonelline protects the cardiocyte from hydrogen peroxide induced apoptosis in H9c2 cells[J]. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine, 2015, 8(4): 263-268.
[10] Folwarczna J, Janas A, Pytlik M, et al. Effects of trigonelline, an alkaloid present in coffee, on diabetes-induced disorders in the rat skeletal system[J]. Nutrients, 2016, 8(3): 133.
[11] Song Q B, Xia X, Ji C M, et al. Optimized flash extraction and UPLC-MS analysis on antioxidant compositions ofNitraria sibirica fruit[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2019, 172: 379-387.
[12] Li X, Yang L P, Liu S Y, et al. Effect of quercetin-3-O-sambubioside isolated fromEucommia ulmoidesmale flowers on spontaneous activity and convulsion rate in mice[J]. Planta Medica, 2014, 80(12): 974-977.
[13] 王丰青, 王丽娜, 智惊宇, 等. 不同品种地黄中毛蕊花糖苷的动态积累规律变化[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2017, 23(24): 78-83.
WANG Fengqing, WANG Lina, ZHI Jingyu, et al. Changes in dynamic accumulation of acteoside from differentRehmannia glutinosa cultivars[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2017, 23(24): 78-83.
[14] 张迪, 张娟利, 马忠英. 毛蕊花糖苷对中波紫外线所致小鼠皮肤损伤的保护作用研究[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2023, 34(1): 57-63.
ZHANG Di, ZHANG Juanli, MA Zhongying. Study on the protective effect of verbascoside on the skin damage induced by UVB in mice[J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology, 2023, 34(1): 57-63.
[15] 赵晶, 张致平, 陈鸿珊, 等. 黄芩甙衍生物的合成及抗人免疫缺陷病毒活性研究[J]. 药学学报, 1998, 33(1): 22-27.
ZHAO Jing, ZHANG Zhiping, CHEN Hongshan, et al. Synthesis of baicalin derivatives and evaluation of their anti-human immunodeficiency virus(hiv-1) activity[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica, 1998, 33(1): 22-27.
[16] 李远志, 王钧冬, 岳朝驰, 等. 野黄芩素在结肠癌发生发展中的作用机制研究[J]. 中国当代医药, 2021, 28(20): 12-16, 20.
LI Yuanzhi, WANG Jundong, YUE Chaochi, et al. Study on the effect mechanism of scutellarin in the occurrence and development of colon cancer[J]. China Modern Medicine, 2021, 28(20): 12-16, 20.
[17] 林惠军, 杨倩, 龚潇. 野黄芩素经Akt/FoxO1信号通路抑制视网膜神经节细胞凋亡[J]. 中南医学科学杂志, 2022, 50(4): 482-485, 490.
LIN Huijun, YANG Qian, GONG Xiao. The mechanism of scutellariae inhibiting apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells via Akt/FoxO1 signaling pathway[J]. Medical Science Journal of Central South China, 2022, 50(4): 482-485, 490.
[18] 王梦娜, 梅茜钰, 陆宾, 等. 野黄芩素改善高糖诱导小胶质细胞活化引起的血脑屏障功能障碍[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2020, 36(11): 1542-1547.
WANG Mengna, MEI Xiyu, LU Bin, et al. Scutellarein alleviates dysfunction of blood-brain-barrier initiated by hyperglycemia-stimulated microglia cells[J]. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin, 2020, 36(11): 1542-1547.
[19] 刘思佳, 吴堃, 任凯强, 等. 柚皮素通过抑制NF-κB-iNOS/COX-2通路减轻小鼠糖尿病肝损伤[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2023, 39(3): 445-450.
LIU Sijia, WU Kun, REN Kaiqiang, et al. Naringin attenuates diabetic hepatopathy in mice by inhibition of NF-κBiNOS/COX-2 pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Pathophysiology, 2023, 39(3): 445-450.
[20] 牛金明, 程莉雅, 吴美美. 柚皮素对过敏性鼻炎模型大鼠鼻黏膜组织TLR4/NF-κB/TNF-α信号通路的影响[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2023, 27(4): 483-488.
NIU Jinming, CHENG Liya, WU Meimei. Effect of naringenin on TLR4/NF-κB/TNF-α signal pathway in nasal mucosa of rats with allergic rhinitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Laboratory Diagnosis, 2023, 27(4): 483-488.
[21] 刘斌, 王叨, 孙霞, 等. 圣草酚对DG-75细胞生长的抑制作用及相关作用机制研究[J]. 中国实验血液学杂志, 2021, 29(6): 1790-1796.
LIU Bin, WANG Dao, SUN Xia, et al. Inhibition effect of eriodictyol to growth of DG-75 cells and the related action mechanism[J]. Journal of Experimental Hematology, 2021, 29(6): 1790-1796.
[22] 杨敏, 张锋, 付姣, 等. 圣草酚对高脂饮食诱导的糖尿病大鼠肝损伤的保护作用及机制探讨[J]. 天津中医药大学学报, 2022, 41(3): 355-360.
YANG Min, ZHANG Feng, FU Jiao, et al. The protective effect and mechanism of eriodictyol on the liver injury in diabetic rats induced by high-fat diet[J]. Journal of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 41(3): 355-360.
[23] 应勤丽, 黄月碧, 杨秀翠, 等. 圣草酚通过抑制TGF-β1/Smad3信号通路改善糖尿病肾病大鼠肾纤维化[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2023, 39(4): 693-697.
YING Qinli, HUANG Yuebi, YANG Xiucui, et al. Eriodictyol ameliorates kidney fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy rat by inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Immunology, 2023, 39(4): 693-697.
[24] 杨舒钧, 梁红亮, 滕俊, 等. 圣草酚对DSS诱导的大鼠溃疡性结肠炎的改善作用及机制探讨[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2022, 38(18): 2188-2192, 2199.
YANG Shujun, LIANG Hongliang, TENG Jun, et al. Ameliorating effect and mechanism of eriodictyol on DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Immunology, 2022, 38(18): 2188-2192, 2199.
[25] 任亚爽, 夏小雯, 王香君, 等. 芦丁镇痛作用机制研究进展及临床应用展望[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2023, 39(5): 807-811.
REN Yashuang, XIA Xiaowen, WANG Xiangjun, et al. Research on analgesic effect and prospect of clinical application of rutin[J]. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin, 2023, 39(5): 807-811.
[26] Li F H, Liao X, Jiang L, et al. Orientin attenuated d-GalN/LPS-induced liver injury through the inhibition of oxidative stress via Nrf2/Keap1 pathway[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2022, 70(26): 7953-7967.
[27] 冯茜, 董波, 杨旭红. 松果菊苷治疗神经系统疾病作用机制的研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2023, 54(5): 1654-1662.
FENG Qian, DONG Bo, YANG Xuhong. Research progress on mechanisms of echinacoside in treatment of neurological diseases[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2023, 54(5): 1654-1662.
Metabolomics study of two different varieties of Asparagus based on LC-MS technique
ZHUANG Hongmei1,ZHAO Jiafen2,WANG Yan3,CHEN Xianzhi4,LIU Huifang1,
HAN Hongwei1, Kelibinuer Kaisaier1, WANG Qiang1, WANG Hao1
(1. Institute of Horticultural Crops, Xinjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences/Xinjiang Vegetable Engineering Research Center/Provincial and Ministerial Co-Construction State Key Laboratory of Crop Stress Resistance Genetic Improvement and Germplasm Innovation in Arid Desert Region/Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Genomic Research and Genetic Improvement of Specialty Fruits and Vegetables, Urumqi 830091, China; 2. Hotan Agricultural Technology Extension Center, Hotan Xinjiang 848000, China; 3.College of Horticulture, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing 210095, China; 4. Wenzhou Vocational College of Science and Technology, Wenzhou Zhejiang 325006, China)
Abstract:【Objective】 Asparagus known as the king of vegetables is the edible tender stem of the asparagus officinalis in the lily family, so this project aims to clarify the two varieties of asparagus transcriptional pathway and metabolism components.The results of this study has provided theoretical basis for in-depth evaluation of nutritional value, development and utilization of germplasm resources and variety breeding of asparagus.【Methods】 A comparative metabolomic study was carried out on the young stems of two varieties of Galande and Jade Pearl asparagus by UPLC-MS and the transcriptional pathway and metabolic components of asparagus were comprehensively understood by comparing the types and contents of metabolic components.【Results】 A total of two hundred and thirty-five different metabolites were screened out accounting for 13.03% of the total metabolites, including fifty-three flavonoids, thirty-nine amino acids and their derivatives, thirty-four phenolic acids, twenty-one lignans, twenty alkaloids, twelve lipids, eight organic acids, seven nucleotides and their derivatives, seven terpenoids, six vitamins, five steroids, four sugars, three coumarins, two ketones, one quinone, one aldehyde, and twelve others. The cyanidin-3-O-galactoside, gallocatechin-(4α→8)-gallocatechin, syringin, sinapine, 2-acetyl-5-methylfuran and quercetin-3-O-sambubioside were higher than those of galactoside. Golande had a high content of glucosyl 5, 8-dihydroxy-2, 6-dimethylocta-2, 6-dienoic acid, N-feruloyl cadaverine, acteoside, 1-O-(6 -o-feruloyl acid) glucoside, 3-O-caffeoyl quinic acid and timosaponin A3-glucoside. 【Conclusion】 Through enrichment of two hundred and thirty-five kinds of metabolites, the main biosynthesis pathways of secondary metabolites include amino acids, cofactors and flavonoids.
Key words:asparagus; LC-MS; metabolism; transcription pathway
Fund projects:“Tianshan Talerts”—Science and technology Innovation Leading Talent project; Major Science and Technology Projects in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region(2022A02005-2);Earmarked Fund for the Basic Scientific Research of Central Government Universities (KYYJ2022001); Xinjiang Vegetable Agriculture Research System(XJARS-07)
Correspondence author: WANG Hao (1970-), male, from Jining, Shandong, researcher, research direction: vegetable cultivation and physiology, (E-mail) wanghao183@163.com
WANG Qiang (1983-), male, from Huining, Gansu, researcher, research direction: Protected vegetable cultivation and physiology, (E-mail) 350615359@qq.com